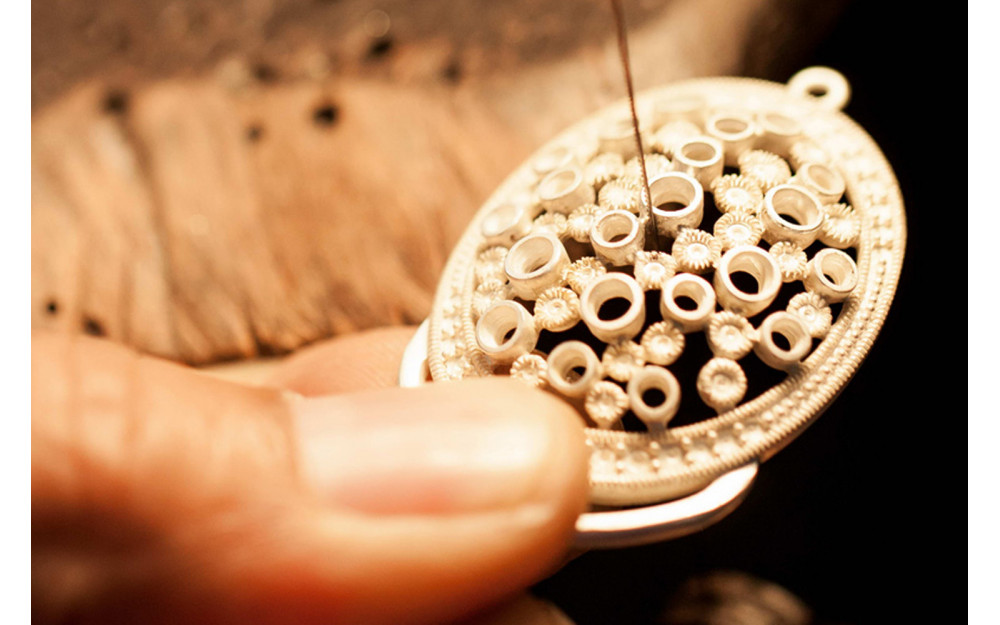
Jewelry is a popular item of adornment and has been for centuries. The manufacturing process of jewelry can be complex, and there are a variety of different methods that can be used. In this article, we will explore the various steps involved in the manufacture of jewelry.
Step 1: Designing
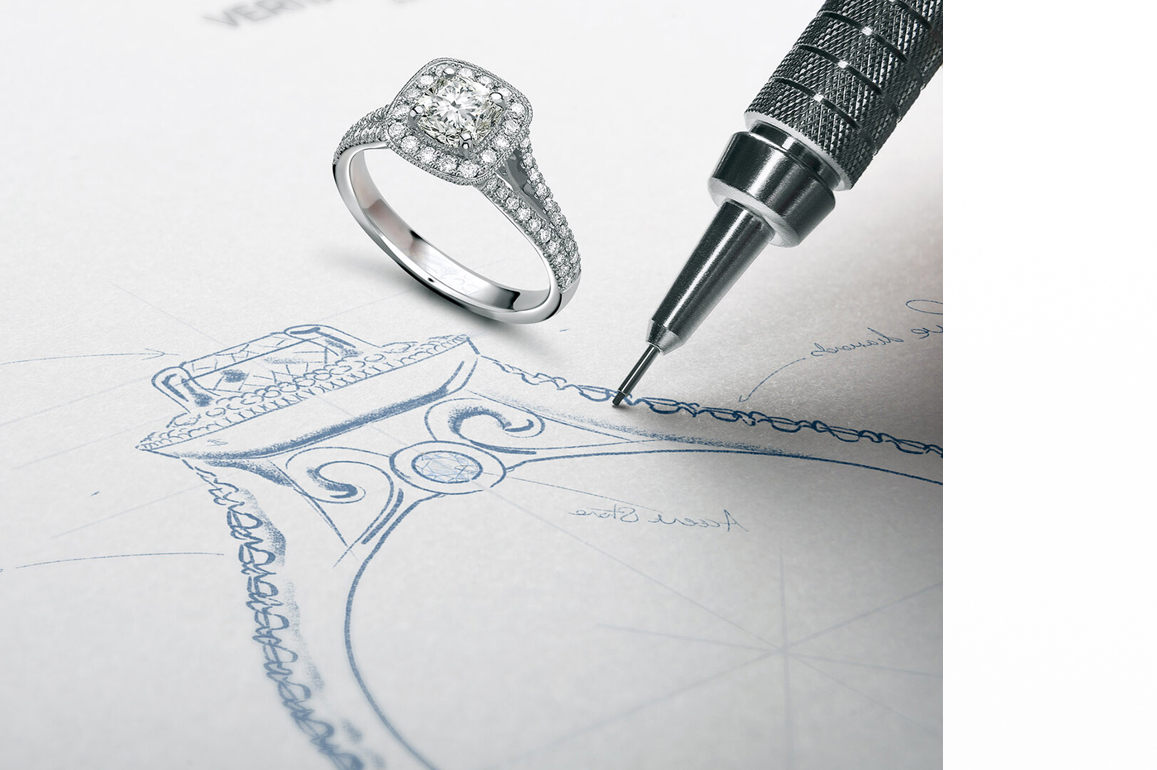

The process of manufacturing jewelry is nothing short of magical! The complete jewelry design process includes several processes, such as designing, model creation, and quality control.
The first stage in the process of creating jewelry is to create a design. The designing stage is where the jewelry designer produces a jewelry design concept and transforms it into a reality by analyzing the concept and additional analysis.
Step 2: CAD/CAM
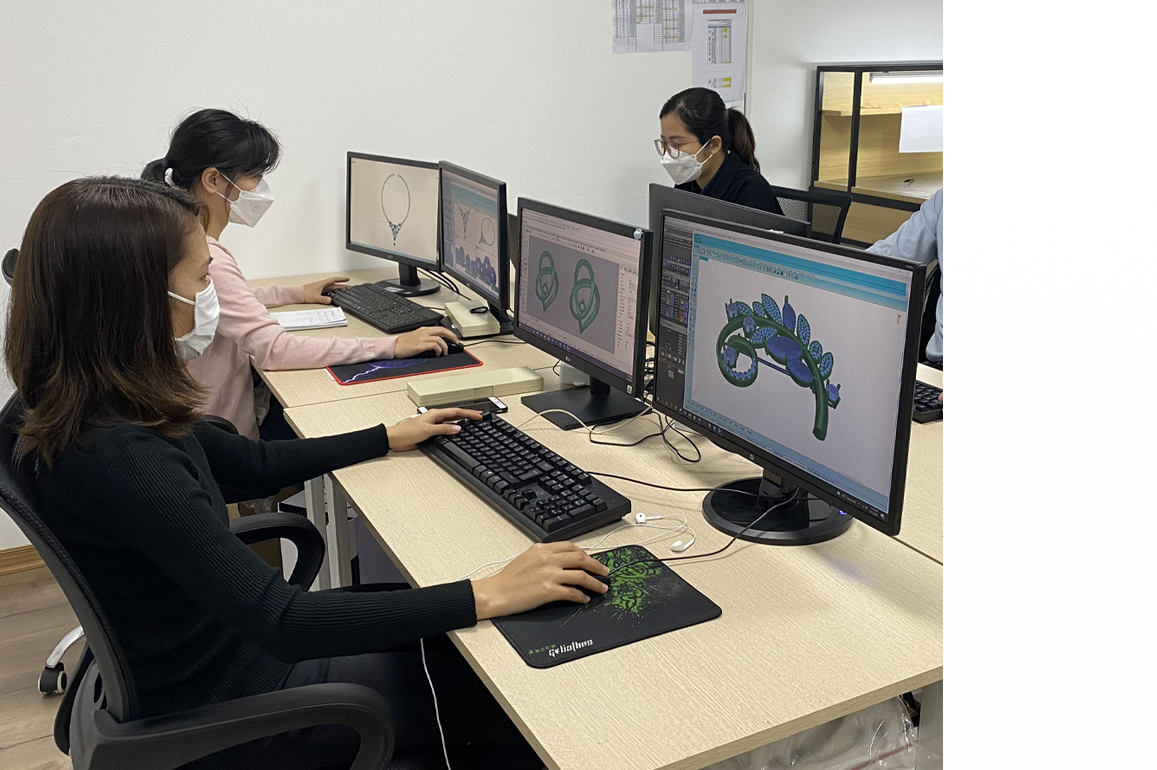

The CAD/CAM step, which occurs immediately following the designing stage, involves the usage of CAD software. The CAD Program is a 2D and 3D computer-aided design software that increases the dimensional accuracy and quality of the design. It also aids in the establishment of a manufacturing database. When the jewellery designer completes the work of developing an idea, it is made on paper and designed in the system. The CAD Software, or Computer Aided Designing technology, is used to convert the 'idea on paper' to the'system.' The CAM, or Computer Aided Manufacture software, is a piece of software that manages the machining and manufacturing processes, or more simply, it automates the production process.
Step 3: Model making
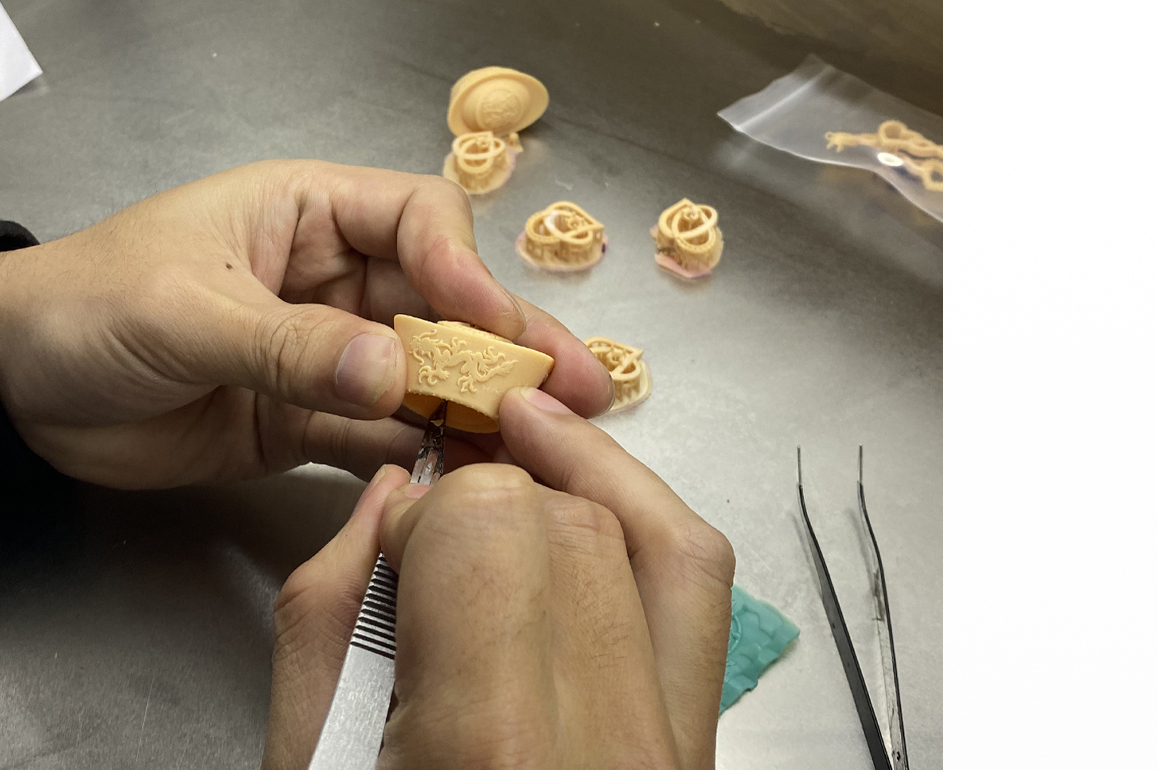

Model Making is the next stage, which involves the process of converting resin output from CAM to silver model (a master design that is used to make comparable pieces of jewelry using a rubber mould) through the casting process.
Step 4: Rubber mould
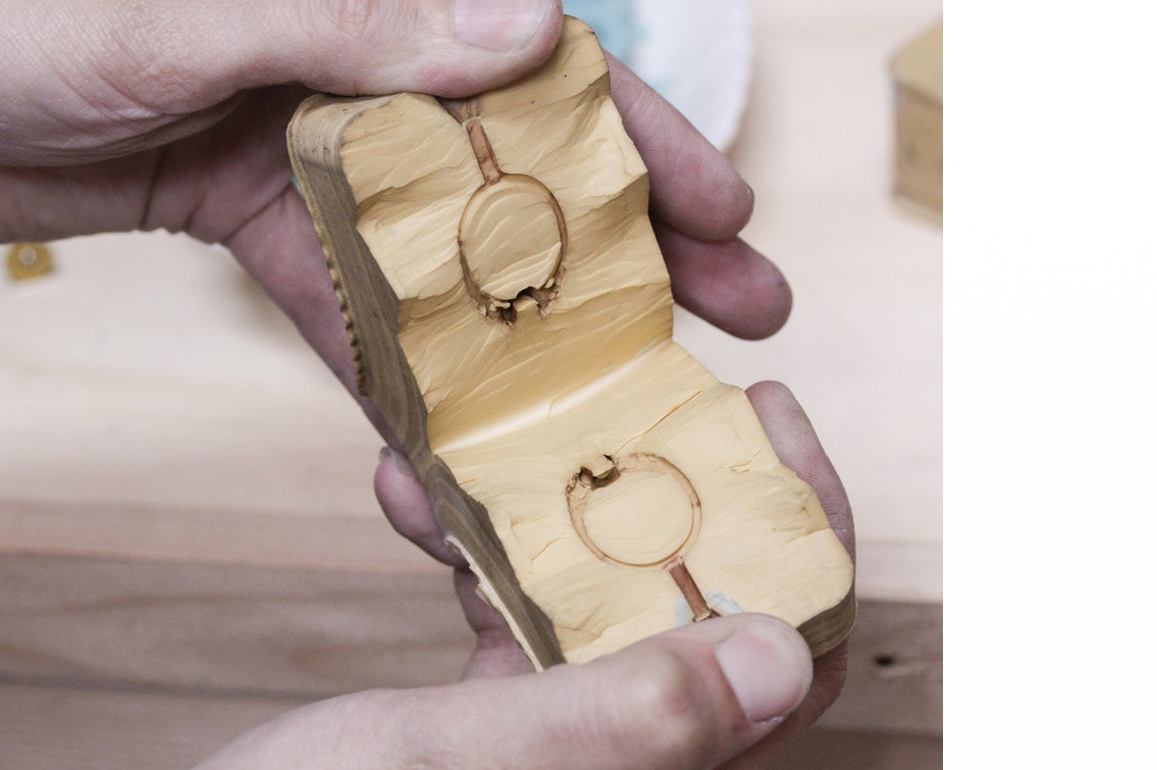

The fourth stage is the Rubber Mould stage, which is critical to the manufacturing process. The Rubber Mould aids in the production of several pieces of identically designed jewelry. The finest aspect about the rubber mould is that the designs remain safe, properly preserved, and imbedded inside it, allowing for future replications of the jewelry design. The materials used to create a mould can range from natural rubber to silicone to metal, and the process is known as vulcanizing.
Step 5: Waxing/ Wax tree
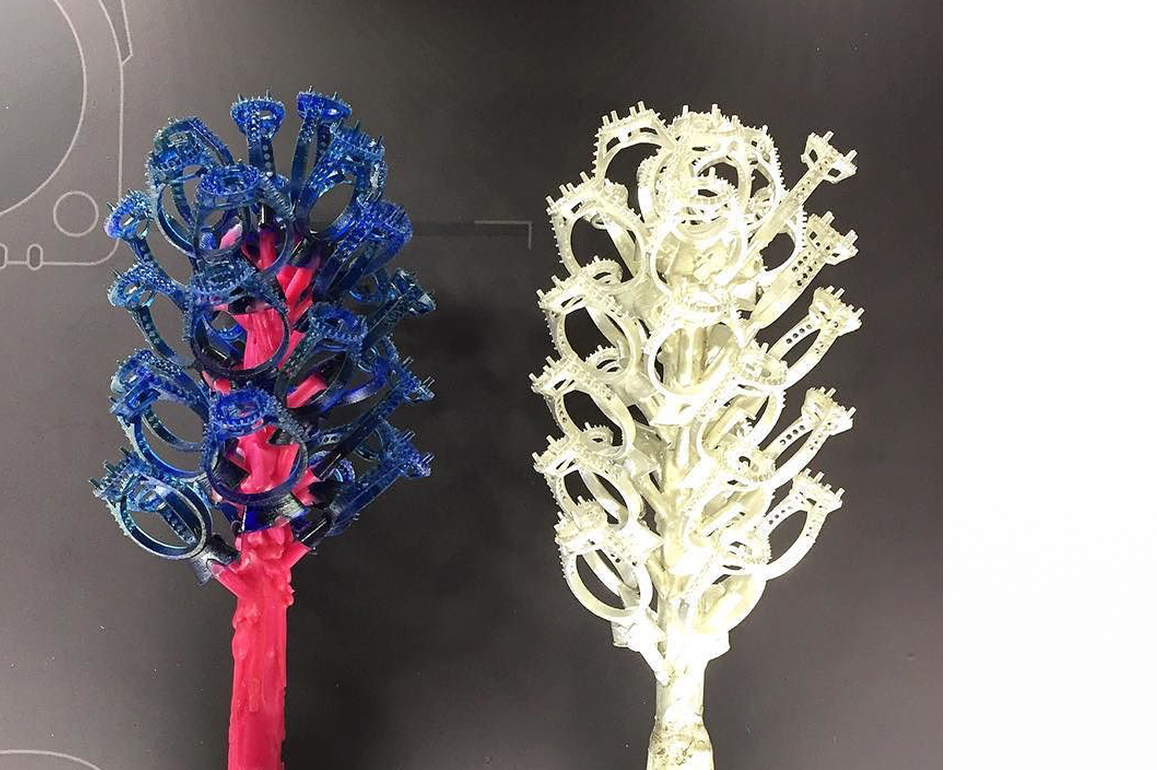

The manufacture of wax pieces is the next stage in the jewelry manufacturing process. The wax pieces are created using silver master rubber moulds. Waxing includes placing the rubber mould on a professional wax injector machine and then injecting pressure into the cavity to generate wax sculptures. These wax models will be utilized in casting.
The soldering of wax components on a wax stem is known as 'treeing.' The treeing procedure involves attaching spruce to each wax piece, forming a 45-degree angle with the stem. Lighter objects are placed at the top of the tree, while heavier items are placed at the bottom.
Step 6: Casting
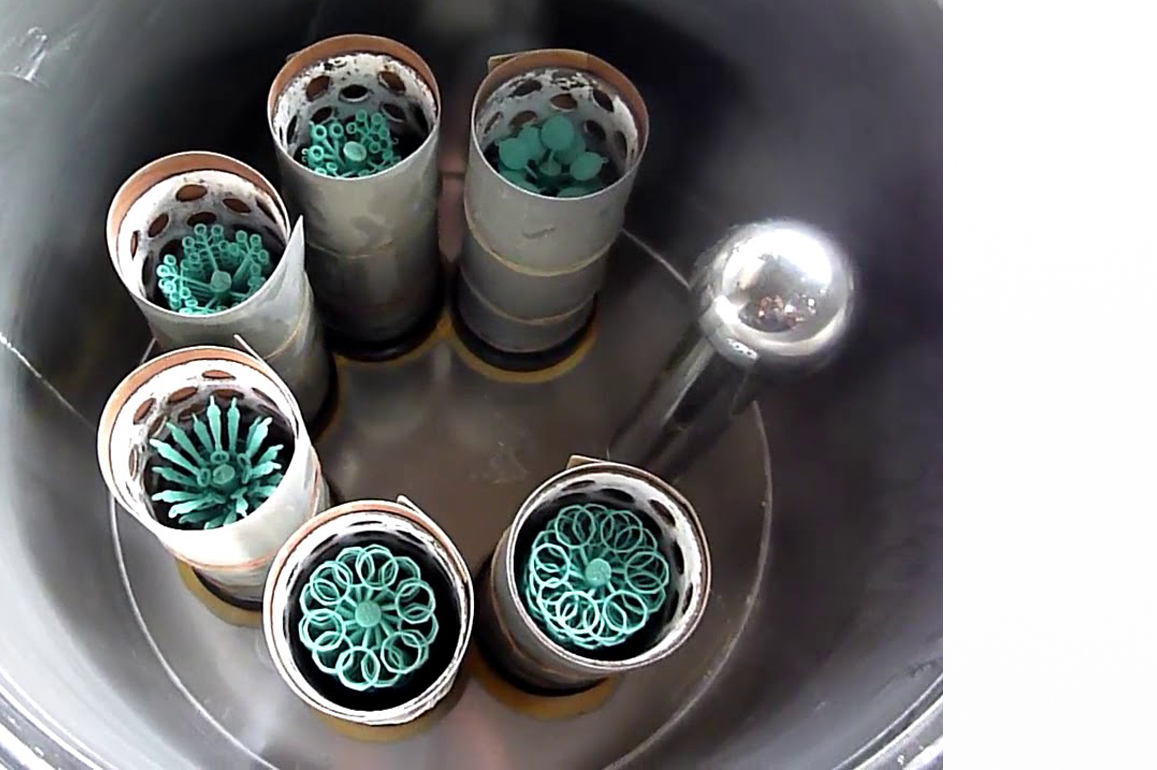

Moving on, the jewelry production process includes the
casting stage, which is regarded as one of the most sophisticated operations.
Casting necessitates the use of knowledgeable and talented casters. The entire
casting process begins with placing the wax tree in a steel flask, followed by
a slurry of chemical powder that takes about an hour to harden. After that, the
flask is heated in an electric furnace. As a consequence, the wax melts,
leaving a hollow in the tree. The molten metal is then poured into the flasks
and allowed to cool. The molten metal is then cooled and destroyed, revealing
the jewelry in the form of casting.
Step 7: Grinding
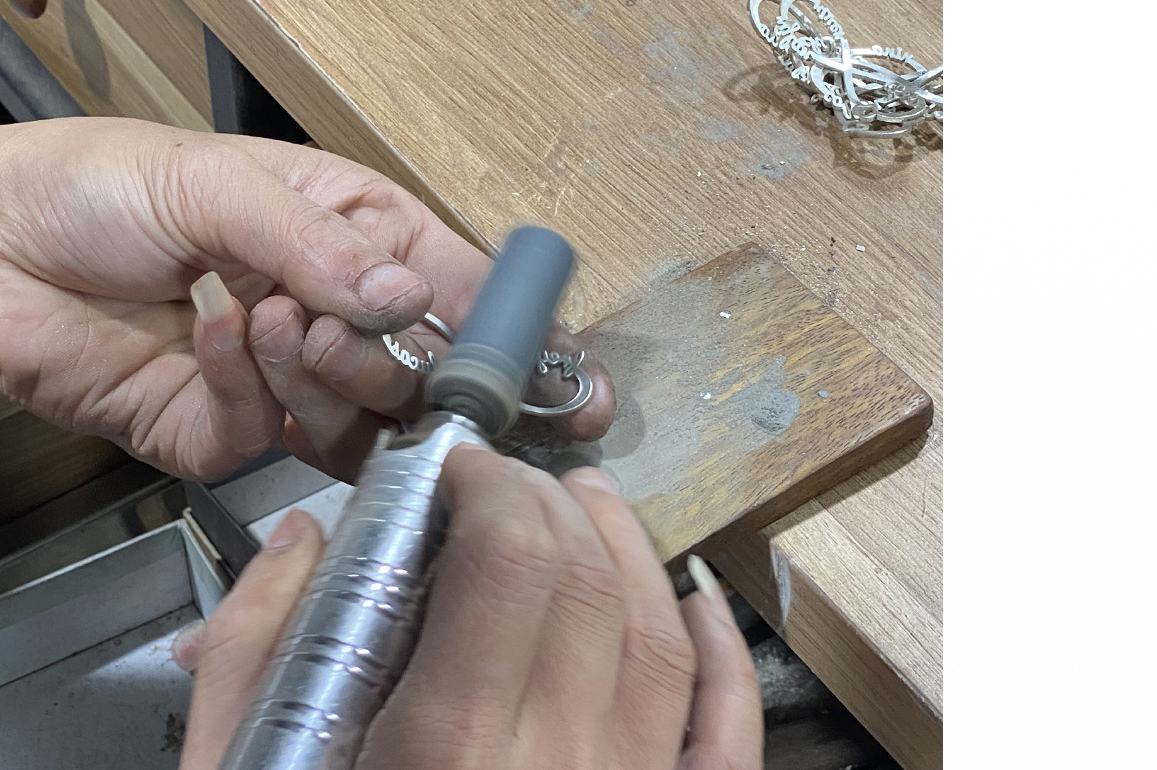

The grinding stage is the next step in the jewelry-making process. The grinding step includes the use of a polisher to remove the nub (A nub is produced after the casting process; after the raw casting is snipped off from the casting tree and appears at the location where the spruce was joined with the gold piece!). The polisher uses a motorized grinding machine to smoothen the surface of gold jewelry. The last polishing step is grinding, which is accomplished by holding the jewelry item against a revolving grinding wheel, resulting in a smooth surface as desired.
Step 8: Filling and pre-polishing
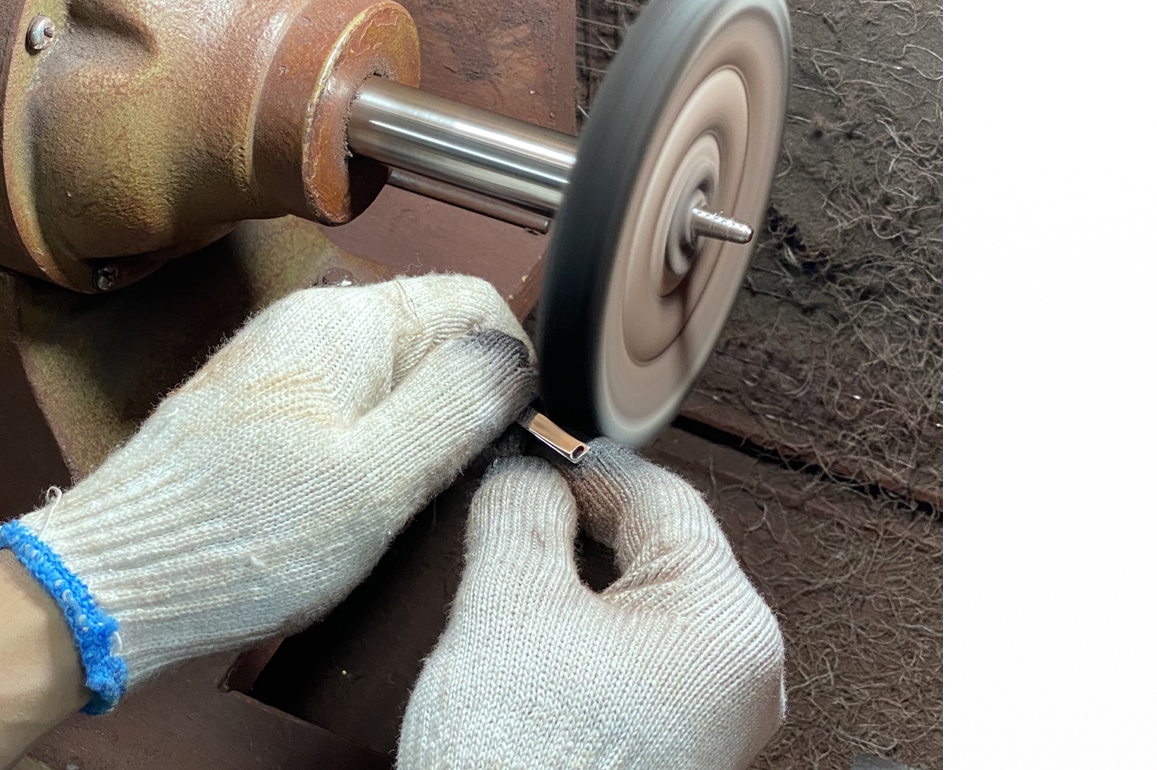

The filing stage is the next step in the jewelry production process. Filing is the process of removing superfluous metal or solder from an item. A range of tools, like as files and burns, are used to remove the casting layer and provide a flawless finish. Following filing, the work of assembly is performed, which is the act of combining two or more components of the same design using the soldering or laser method.
Following that, polishing is done to produce a tidy and exquisite finish, increasing the value of the jewelry piece. Tumbling, pre-polishing, and hyper cleaning are the three procedures involved in the polishing stage. It is important to note that before the diamond is set, those jewelry items including diamonds require pre-polishing, because the diamond sections cannot be polished once the diamonds are placed below the region, as this may jeopardize the diamond's luster.
Step 9: Metal setting
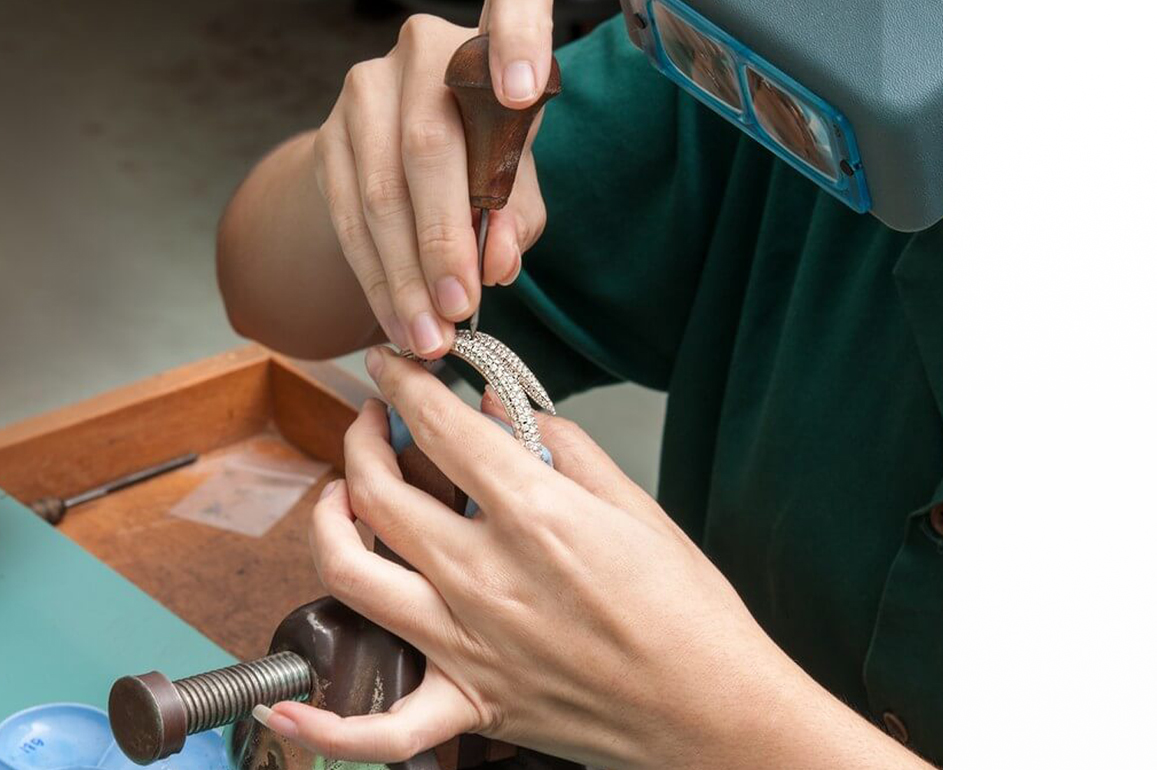
The metal setting is the ninth stage in the production of jewelry. The procedure of setting or mounting a gemstone in jewelry is known as metal setting. The metal setting is changed to produce different designs. A mix of different metal settings is also employed to give the jewelry item a striking appearance. As previously said, metal settings come in a variety of styles, including prong, plate prong, pave, bezel, pressure, bead, flush, invisible, fishtail, miraculous plate, and channel.
Step 10: Polishing
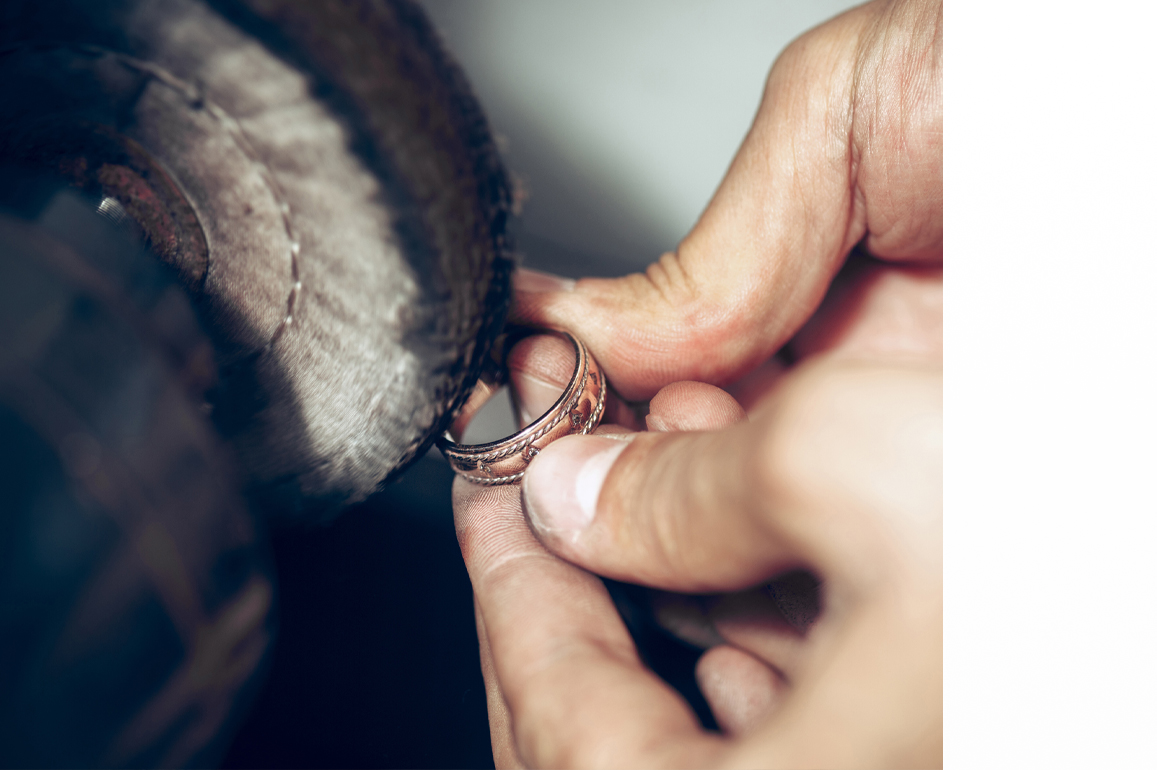

The polishing step is the final stage in which the jewelry is polished. Polishing is done to guarantee that the jewelry shines better once the stones have been placed. Both hand and machine polishing methods are available. Soft buff, solid buff, hair buff, single line ball buff, coin buff, platinum polishing rouse, red and green rouse (to impart shine), black lustre to remove casting or filling layers, and white luster to eliminate roughness are some of the instruments that enable the artisans polish the jewelry manually.
Step 11: Quality control
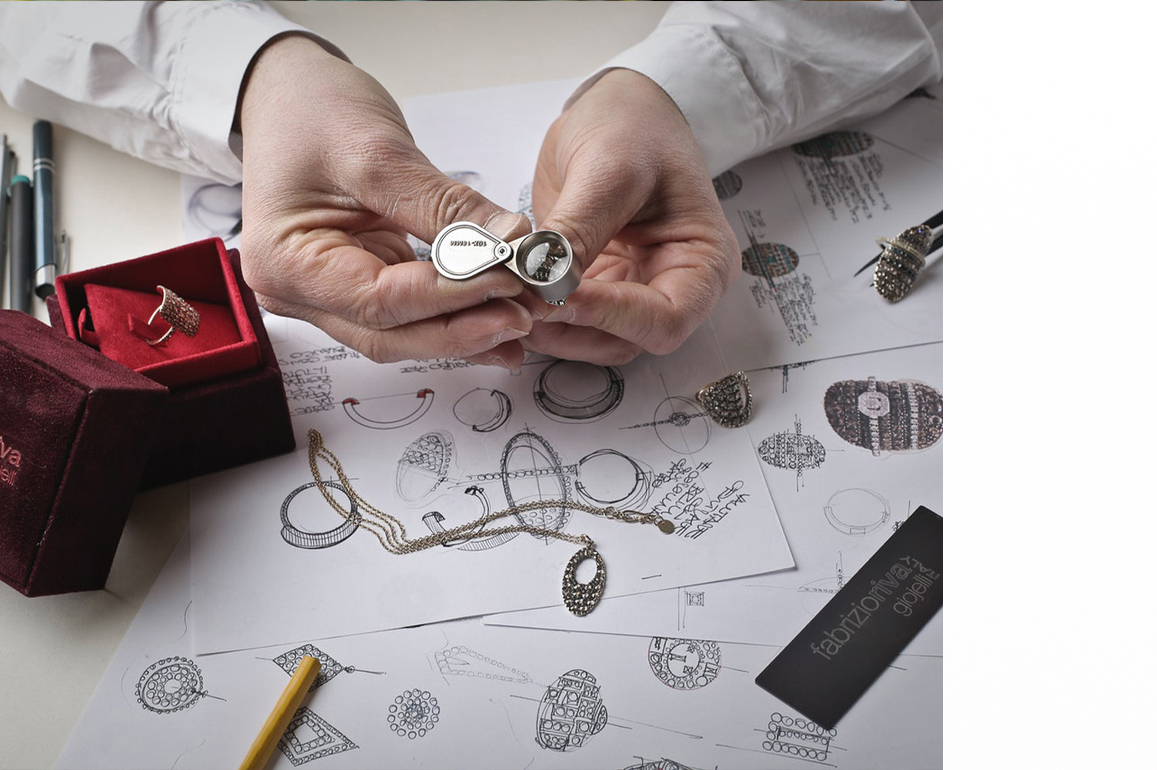

The final stage in the jewelry production process is
quality control, which is just as crucial as the other phases. Quality control
is the step in which the final manufactured product is ensured to comply to the
stated set of quality rules and fulfill the standard criteria. Quality control
employs three methods: measurement, visual inspection, and mechanical
inspection.



